Deciphering the Enigma Code of the Brain One of the current challenges of neuroscience is to decipher the neural code, the language of the brain that is translated into movement This is a fundamental step to be able to program devices that allow paralysis to be treated and to produce a new generation of prosthesesExplore Sally Foster's board "Encryption and Code Breaking", followed by 359 people on See more ideas about coding, cryptography, ciphers and codesEnigma works via a system of transposition, ie replacing letters with others in the alphabet based on a preset table If you replace A > U, and B > T etc the message becomes unreadable unless you have the template for decoding it However enigma did far more than a simple transposition (which is incredibly easy to crack)
Cryptology I Vigenere Based Systems
Easy alphabet enigma code
Easy alphabet enigma code- The mathematical prowess of the Polish Cypher Bureau had secretly first broken Enigma codes in 1932, with the aid of French intelligence At the eve of the war they handed their work to the AlliesAlphabet The display windows at the top of Figure 1 show the letters JLY The three encoding is reversible also makes life easier for anyone trying to break the Enigma code Breaking the Enigma code which were easy to guess if you knew the weather at the point of transmission




Substitution Cipher Wikipedia
The Enigma was constantly updated throughout the war, so the exact types of settings variedHowever, they usually included The rotors The Enigma M1 had three rotors that the operator could choose from from a pool of 5, though this number was later increased to 8 (and a machine with 4 rotor slots was released toward the end of the war) YouPegged inflow at $1 mnThe Enigma rotor cipher machine was potentially an excellent system It generated a polyalphabetic substitution cipher, with a period before repetition of the substitution alphabet that was much longer than any message, or set of messages, sent with the same key A major weakness of the system, however, was that no letter could be enciphered to itself
So initially, the total number of inputoutputs for the Enigma Machine (individual monoalphabetic ciphers) was 6 326!Answer http//wwwsupercomputingchallengeorg/0607/finalreports/63pdf How do you write an enigma code? The Germans began using the Enigma machine in the late 19s By late 1932, the Poles had broken the Enigma code In 1939 just a matter of weeks before Hitler invaded Poland, the Polish Cipher Bureau shared its technology with the French and the British, who continued to decode messages
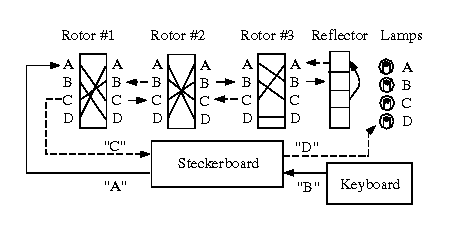
Enigma CS61B fa21 classproject The Enigmas effect a substitution cipher on the letters of a message That is, at any given time, the machine performs a permutation—a onetoone mapping—of the alphabet onto itself The alphabet consists solely of the 26 letters in one case (there were various conventions for spaces and punctuation)Because all you have to do to decode it is do the process all overThis is somewhat simpler than the real Enigma machines that used three or four rotors which could be rearranged and selected from a selection, and generally featured a plugboard as well However, we do use an alphabet with n=72 instead of n=26, so



Project 1 Cs 61b Fall 16



Project 1 Cs 61b Fall 19
And so on, through the alphabet Now, when you write your message, every time you have the letter A, you replace it with a Z, when you have a letter B, you replace it with a Y But there's some bad news about this code Not only is it easy to encode, it's easy to decode, too!10 Codes and Ciphers Commonly Used in History Code language has been used to safeguard and conceal important messages for thousands of years As time progressed, complex codes have been created since simple codes are easily decoded Codes and ciphers are not the same In code, each word in the message is replaced by a code word or symbolEnigma Enigma was a ciphering (code communication) system used by the German military from 1926 until the end of World War II, and by several other nations for some years after Enigma was the first mechanized messageencryption system to see wide use Enigma produced such thoroughly scrambled messages that for many years its cipher was




Codes And Ciphers Complete Top 10 Codes Keys And Ciphers Wattpad




Enigma Encoder 101 Computing
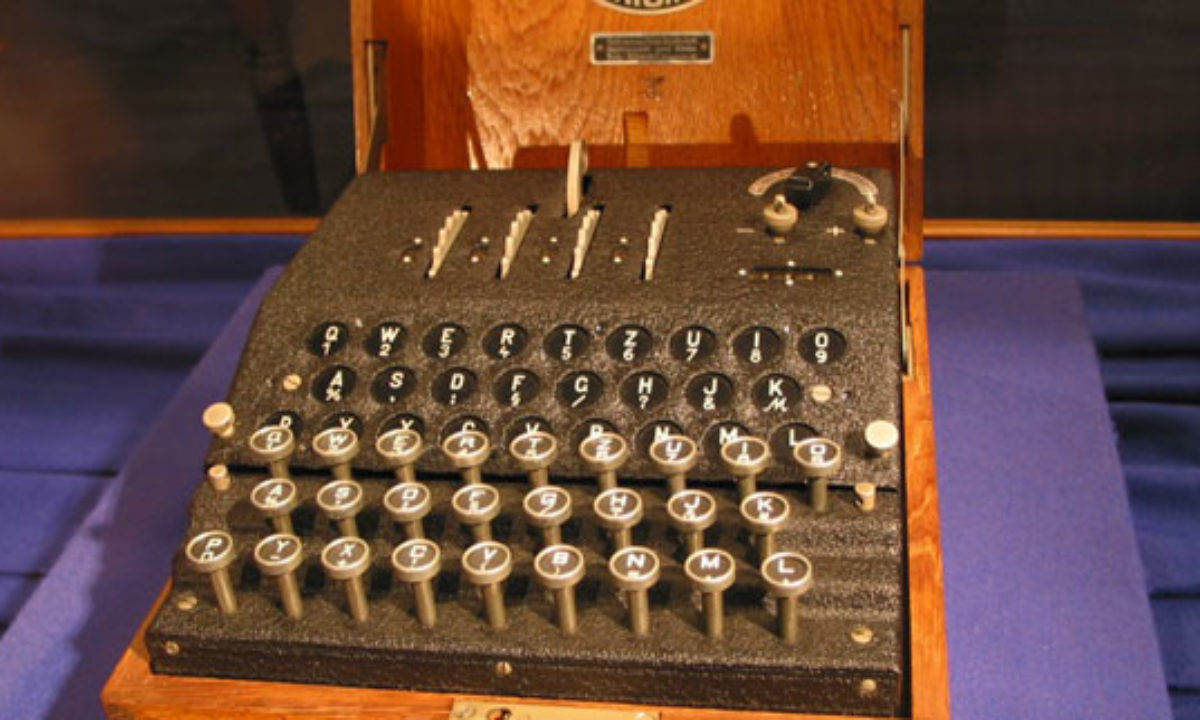
Instead, every letter of the alphabet has been replaced by a number, the same number representing the same letter throughout the puzzle All you have to do is decide which letter is represented by which number!One would wonder why the encryption mattered anyway, and why it took a lot of effort to decode it The quality of codes is determined by the number of possibilities of getting the correct answer In the case of the Enigma code, one had to get all settings on the Enigma machine right before you could decode it An original German Enigma code encryption machine, at Bletchley Park Museum, England The efforts of Alan Turing and others to crack the code, using early computers, was crucial to the Allied war




Digitalocean Blog



How The Allies Cracked The Enigma Code By Karthick Nambi Lessons From History Medium
Colossus The electronic codebreaker was used for the Lorenz machine though The Enigma machine used mechanical "Bombes" 1 level 1 praguepride 3y IIRC it wasn't that it was impossible to crack but there were just so many combinations that by the time a code was cracked it was hours or days past usefulness 7 The need to conceal the meaning of important messages has existed for thousands of years Over time, people have found increasingly complex ways of encoding their messages as the simpler ways are decoded with greater ease Contrary to laymanspeak, codes and ciphers are not synonymous A code is where each word in a message is replaced with a code word orTo start you off, we reveal the codes for two or three letters




How To Decipher A Secret Code 13 Steps With Pictures Wikihow



1
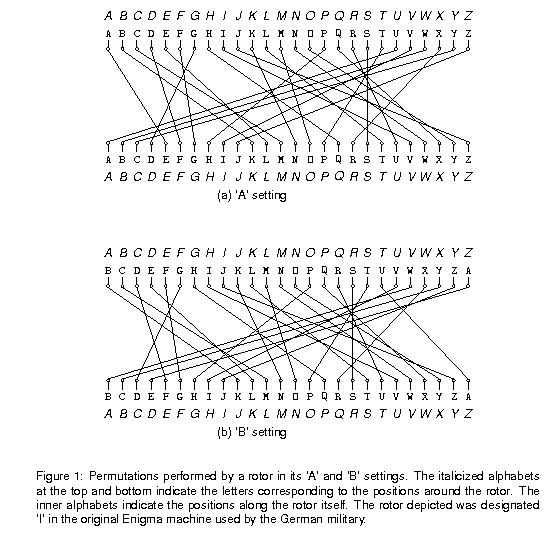
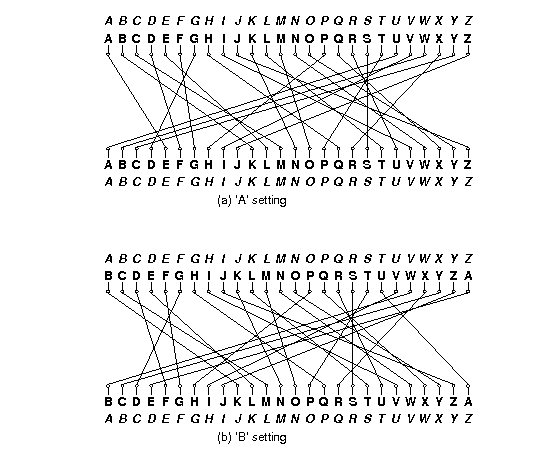
ENIGMA Chapter 1 – Historical Background ENIGMA Chapter 2 – The Invention of the Enigma Machine The Enigma machine is a polyalphabetic substitution cipher machineThis post will provide a little background information on the differences between monoalphabetic and polyalphabetic substitution ciphers and on the specific characteristics of cipher alphabets created by an Enigma The key to a successful simulation of the ENIGMA machine is to know the internal wirings of the rotors (or "wheels"), shown below The rotors are labeled I through VIII, b, and g The letters of the alphabet in order represent the input, and the wiring for each rotor indicates the transformation for each letterEasy as 1, 2, 3 This all seems very clever, but so far it's all been letters and no numbers So where's the maths?



The Imitation Game How Did The Enigma Machine Work Science Abc




The Enigma Cipher Machine And Breaking The Enigma Code
To encrypt your message with an Enigma machine, you would 23 October 21 Codewords are like crossword puzzles but have no clues! Have your child follow these easy steps to use the Caesar Cipher Step 1 Write out the entire alphabet in a line Step 2 Choose a number to be your "rotation" amount In this example, it is 7 Count this many letters into the alphabet Step 3 Under your first line, starting at the letter you "rotated" to, rewrite the alphabet




Pin On Cryptography




Substitution Cipher Wikipedia
What Made the Enigma Code Special?However, this number is only a measure The encryption code returns an element from the alphabet array The Caesar cipher is probably one of the most basic ciphers, although it was the basis of the Enigma code




11 Cryptographic Methods That Marked History From The Caesar Cipher To Enigma Code And Beyond




Pigpen Alfabeto De Linguagem Gestual Mensagens De Celular Mais Engracadas Codigo Do Alfabeto
Enigma's Secrets How it Worked and How the Code was Broken By way of introduction, see the Historical Background to Enigma and the Key Players Involved The Working Principle The Enigma machine basically provided a simple substitution of a plaintext symbol with a different ciphertext symbol generated by the machine What made the machine special however was that Enigma was a machine with an input key that takes input and sent it via a preconfigured set of rotors and outputs an alphabet The rotors configuration is made more complicated by a wiring Speakeasy The Alphabet of Coding Eye News,The Indian Express PANDORA PAPERS Family behind premier hospital in Delhi set up offshore firm with assets worth $35 mn Offshore footprint found in origins of IPL teams Rajasthan Royals, Kings XI Punjab Exchief of Military Intelligence and son set up firm in Seychelles;




How The Allies Cracked The Enigma Code By Karthick Nambi Lessons From History Medium




Digitalocean Blog
Enigma decoder Decrypt and translate enigma online The Enigma cipher machine is well known for the vital role it played during WWII Alan Turing and his attempts to crack the Enigma machine code changed history Nevertheless, many messages could not be decrypted until today Trifid cipher Text to binary Text to base64The maths comes if you think of the letters as numbers from 0 to 25 with A being 0, B being 1, C being 2 etc Then encoding, shifting the alphabet forward three places, is the same as adding three to your starting number Enigma machines use a form of substitution encryption Substitution encryption is a simple approach to encrypt communications, but it's also pretty easy to crack A Caesar cypher is a simple example of a substitution encryption technique Each letter of the alphabet is shifted to a certain number of places in a Caesar cypher



Why Did The German Nazis Decide To Design Enigma So That It Wasn T Possible To Map A Plain Text Character To The Same Character In The Cipher Text Quora




Cryptanalysis Of The Enigma Wikipedia
This code made a few breaks back in my spare time There are, however, a few alterations to the original machine that this simulation shows, one being The enigma machine was used in World War II to encrypt secret messages The Enigma machines are a series of electromechanical rotor cipher machines The first machines were invented at the end of World War I by German engineer Arthur Scherbius and were mainly used to protect commercial, diplomatic and military communication Enigma machines becameThis paper includes a C program that simulates Enigma, and a method to break its code The latter is achieved by a simulation of a simplified Bombe, a mechanical device that was actually used during WWII at Bletcheley Park, a site in England where a major deal of the work on breaking Enigma's code was done




The Imitation Game How Did The Enigma Machine Work Science Abc
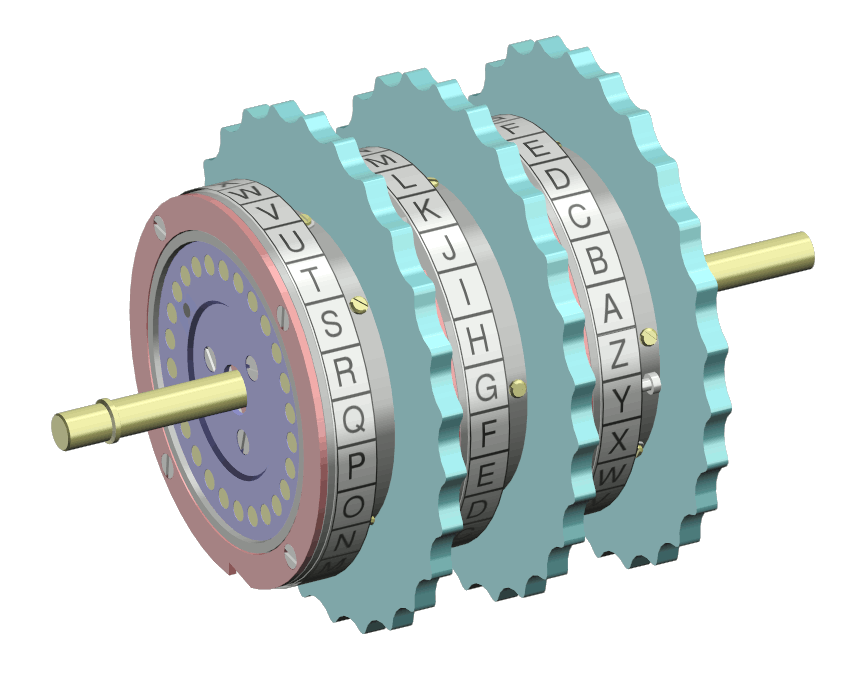



Rotor Machine Wikipedia
It is completely impossible to create an impossible code However most people come up with a very simple code'a' = 'b', 'b' = 'c' and so on The famous enigma code did not do this It came up with an alternative way to substitute letters Here is a simplistic version of itSimplified Enigma machine that is limited to a six letter alphabet Figure 4 Simplified version of a Enigma machine with one rotor The disk on the left is the keyboard, the middle ring is the rotor, and the disk on the right is the lampboard The wiring of the rotor determines how the plaintext letters will be encryptedˇ106 1016 By 1939, increases in the number of rotors and plugboard pairs had increased this gure 159 10 As you can imagine, breaking the enigma code was quite a task!




Top 10 Codes And Ciphers Listverse



During The Second World War How Did The Germans Around The World Knew The Daily Combination Of Letters For Decoding Enigma Quora
Answer (1 of 5) Enigma was particularly difficult to break because it combined two different types of encryption, each of which had different vulnerabilities The rotors take in a letter and output a different letter, then rotate so that the encryption pattern is different for each time a letteThe Phonetic Alphabet and Morse Code poster by Zapista OU Our posters are produced on acidfree papers using archival inks to guarantee that they last a lifetime without fading or loss of color All posters include a 1" white border around the image to allow for future framing and matting, if An Enigma machine is a famous encryption machine used by the Germans during WWII to transmit coded messages An Enigma machine allows for billions and billions of ways to encode a message, making it incredibly difficult for other nations to crack German codes during the war — for a time the code seemed unbreakable Alan Turing and other researchers exploited a




Rotor Machine Wikiwand




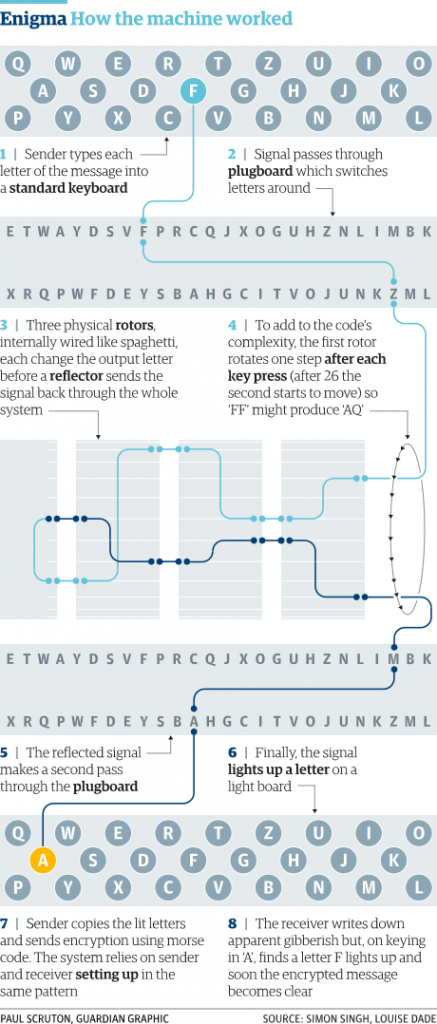
How Did The Enigma Machine Work Computing The Guardian
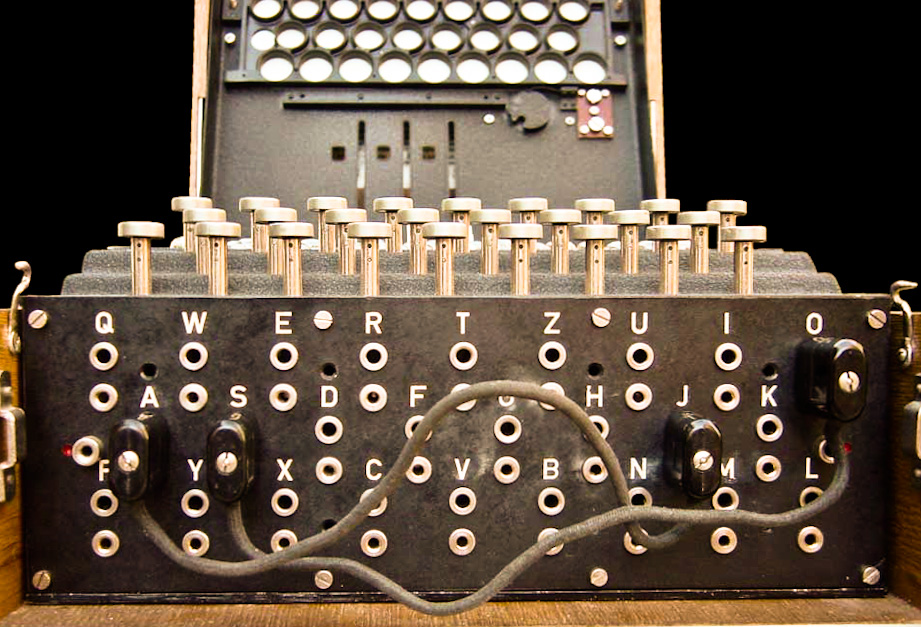
Use your understanding of the English language to deduce which letter of the alphabet should be allocated to which number When you have allocated a letter to a number add it into the relevant numbered box in the grid below the Enigma code That letter will automatically appear in all of the corresponding numbers on the main grid Enigma has an electromechanical mechanism for the rotor which scrambles the alphabet's 26 letters One person in normal usage enters text on the Enigma keyboard and another person writes down which of the 26 lights above the keyboard lights up at each press key If plain text is entered, the encoded ciphertext shall be the litup lettersA code is a system of symbols, letters, words, or signals that are used instead of ordinary words and numbers to send messages or store information o Learn more about the code machine, ENIGMA, Write one letter of the alphabet in each division on each wheel Then attach the two wheels together using a split pin so that you can rotate



The World According To Benedict Cumberbatch Enigma Chapter 3 The Substitution Cipher



The Polish Attack On Enimga
Code Wheel for encrypting and deciphering messages This activity can be easily differentiated to accommodate different ages and abilities The idea is to use two circles to create a Code Wheel to encrypt and decipher messages What you need Easier version Circle Templates printed on card Scissors Pencils/pens Split pins Harder version CardBuild your own Enigma These pages are about an electronic replica of the famous Enigma cipher machine, that you can build yourselfIt is known as the EnigmaEIf you already own an EnigmaE but haven't yet registered it, now may be the time to do soIf you have any questions whilst building the kit, you might want to check the FAQ or visit the special support pageThe Caesar cipher encrypts by shifting each letter in the plaintext up or down a certain number of places in the alphabet If the message was right shifted by 4, each A would become E, and each S would become W like the Enigma machine but once the code is broken, it's extremely easy to figure out the plaintext The Caesar cipher is



Enigma Machine Kata




Code And Ciphers Julius Caesar The Enigma And The Internet
The three rotors in the Enigma machineSourceWikipedia The military Enigma Machine had another set of encryption layers by using switchboards where each alphabet got mapped to another alphabet In 1923, the German Navy used its own Enigma machine and by the 1930s, it became standard equipment by the German Intelligence divisions In October 13, a 1944 German Enigma machine was




Top 10 Codes And Ciphers Listverse



Enigma Procedure




Project 1 Enigma




The Imitation Game How Did The Enigma Machine Work Science Abc




Enigma Machine How Does The Famous Encryption Device Work Dev Community




Enigma Machine Simple English Wikipedia The Free Encyclopedia




The Human Errors That Defeated Enigma Openmind




The Enigma Enigma How The Enigma Machine Worked Hackaday



Understanding The Enigma Swimming The Styx




Cryptology I Vigenere Based Systems




Ic211 Oop And Enigma




Enigma Machine Brilliant Math Science Wiki




Enigma The German Cipher Machine




The Enigma 1




1 2 3 Code Cycle 3 Activities Lesson 3 4 How To Ensure A Message Is Secure Le Site De La Fondation La Main A La Pate
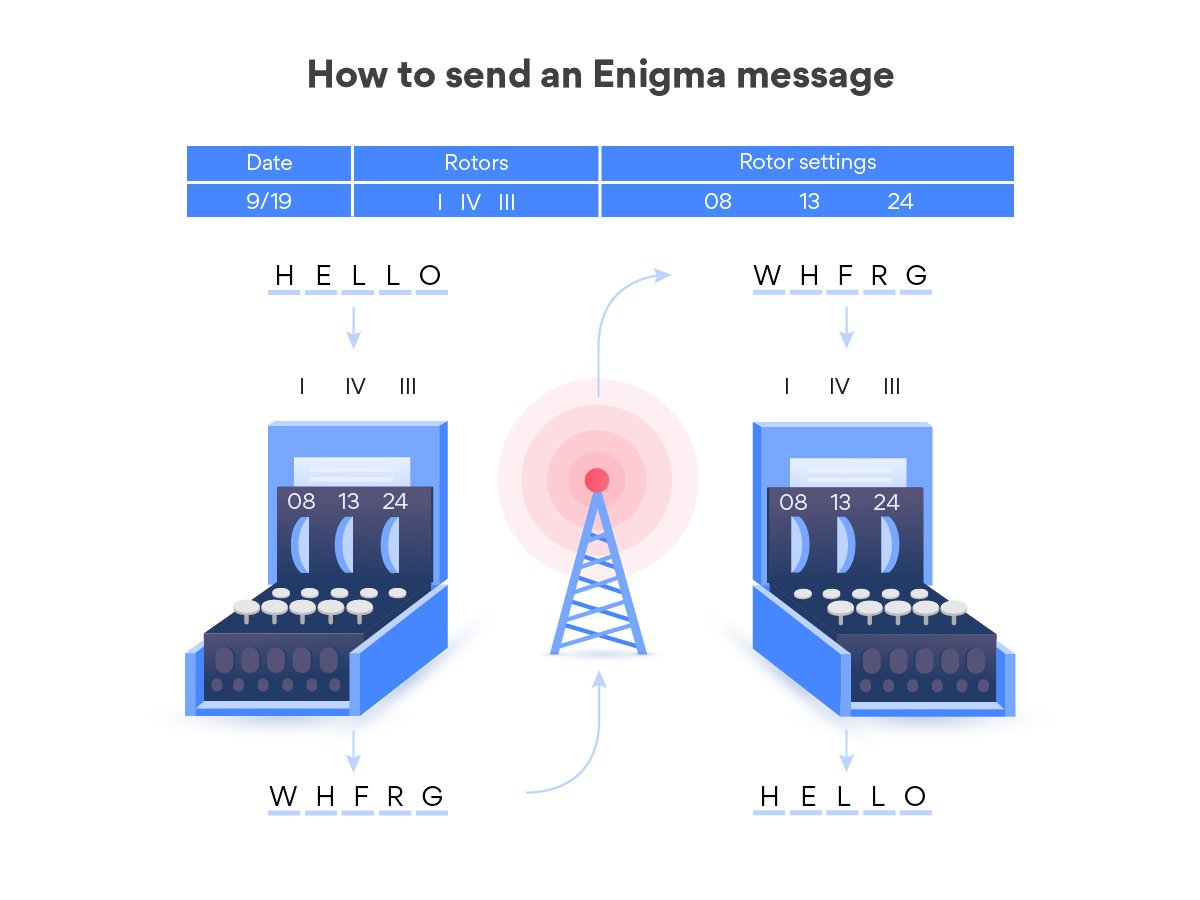



How The Allies Cracked The Enigma Machine Nordvpn
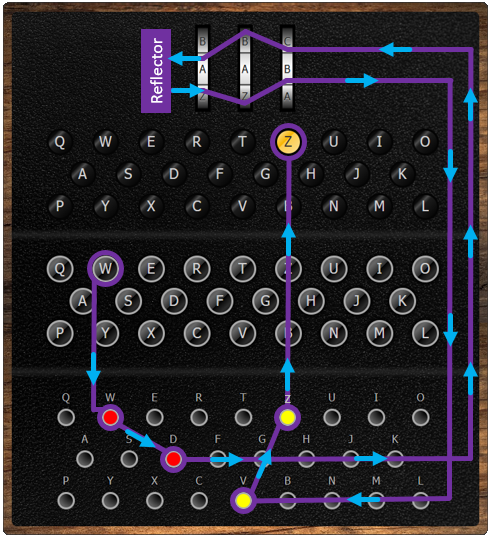



Enigma Encoder 101 Computing
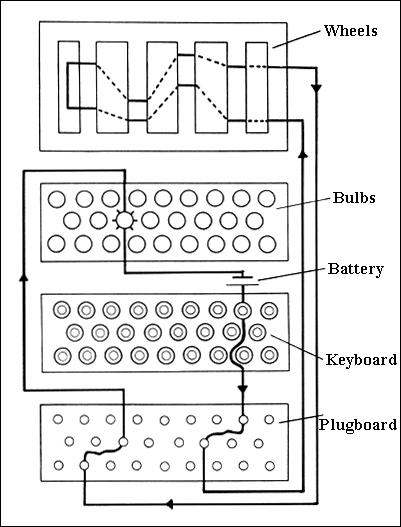



Enigma Machine




How To Build An Enigma Machine Virtualisation In Python By Vasile Păpăluță Analytics Vidhya Medium
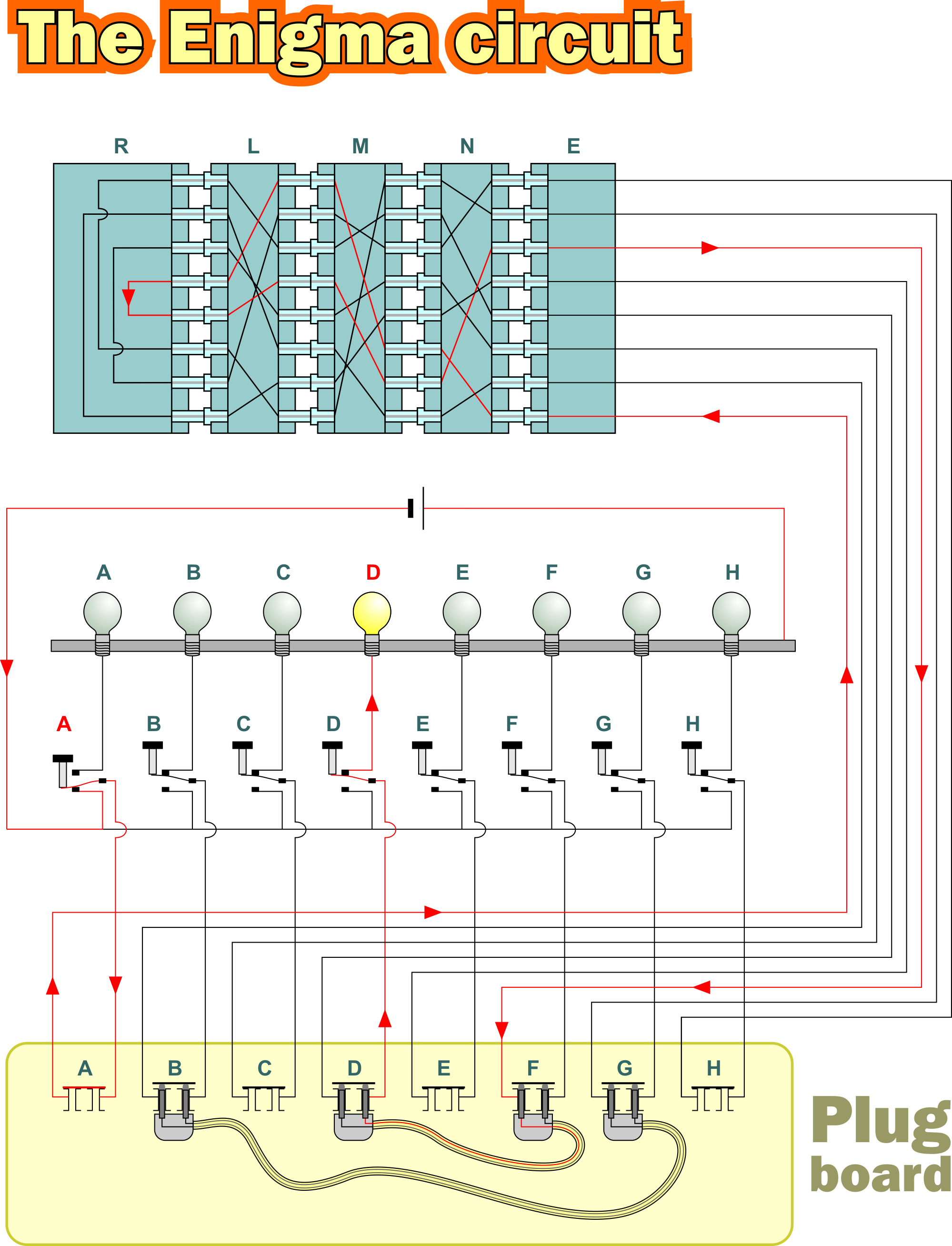



Enigma The German Cipher Machine




Kid S Game To Arduino Enigma Machine 10 Steps With Pictures Instructables
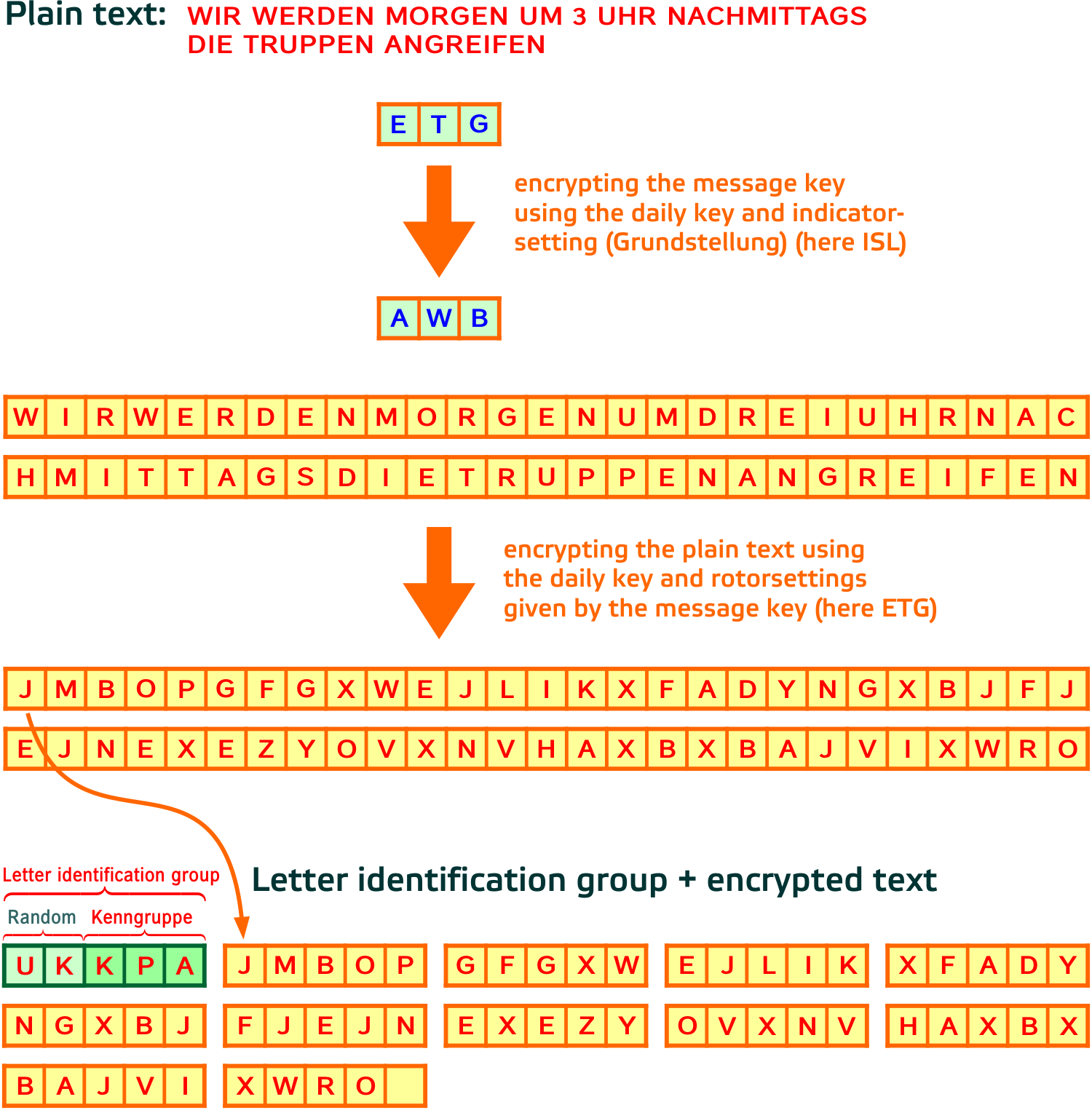



Enigma The German Cipher Machine




Enigma Code Breaking Replicating A 1930s Polish Cyclometer Hackster Io




Kid S Game To Arduino Enigma Machine 10 Steps With Pictures Instructables



Web Stanford Edu



Enigma Procedure




Four Integrated Enigma Theme Ciphers Elgar S Enigmas Exposed




Cipher Machines Columbus State University




Exploring The Enigma Plus Maths Org




The Enigma Enigma How The Enigma Machine Worked Laptrinhx




Charlesreid1




Enigma Machine By 101computing Net



Web Stanford Edu
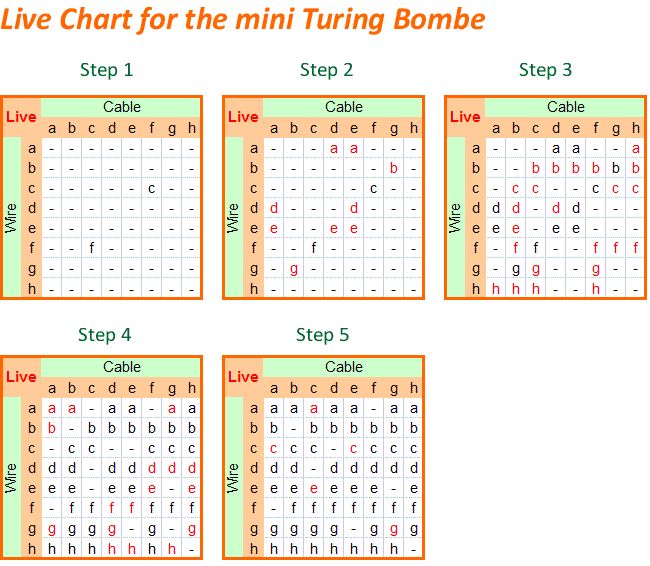



Enigma The German Cipher Machine



Web Stanford Edu




How To Crack The Enigma Code Calculate
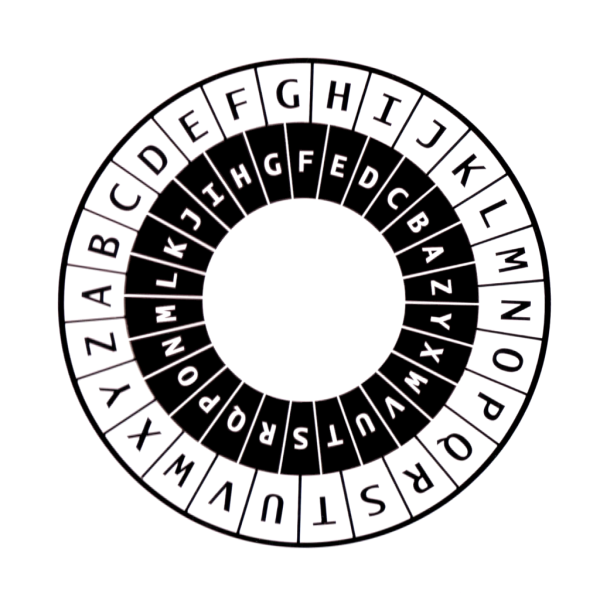



5 0 The Mechanization Of Ciphers



Enigma Details



Alan Turing




Poland S Pre War Code Crackers Science In Depth Reporting On Science And Technology Dw 19 02 15




Code Breaking Instrumental In Ending World War Ii American Association For The Advancement Of Science
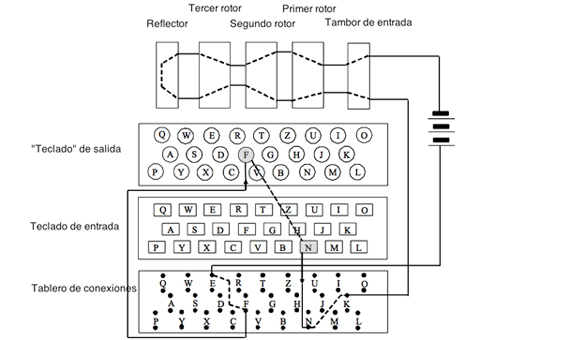



The Human Errors That Defeated Enigma Openmind



The World According To Benedict Cumberbatch Enigma Chapter 3 The Substitution Cipher




The Enigma Cipher Machine And Breaking The Enigma Code




Decoding The Project Languages Code And Ciphers Richard Gallon We Are Here




Ukw D
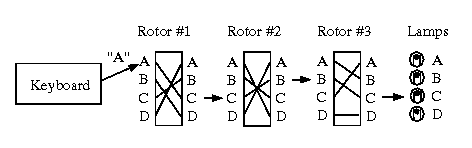



Cryptology I Vigenere Based Systems



Web Stanford Edu




Building The Enigma Machine In Swift Agostini Tech




Building The Enigma Machine In Swift Agostini Tech
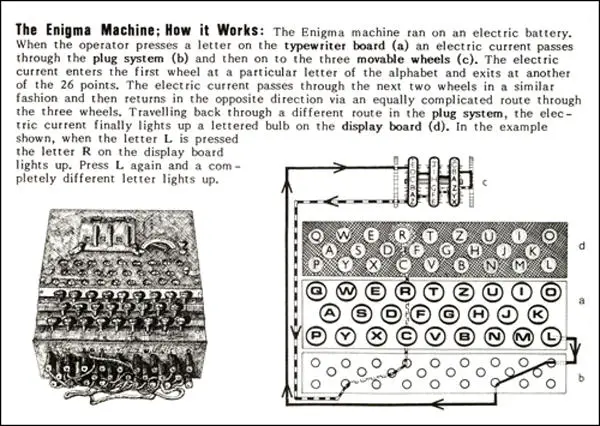



Enigma Machine
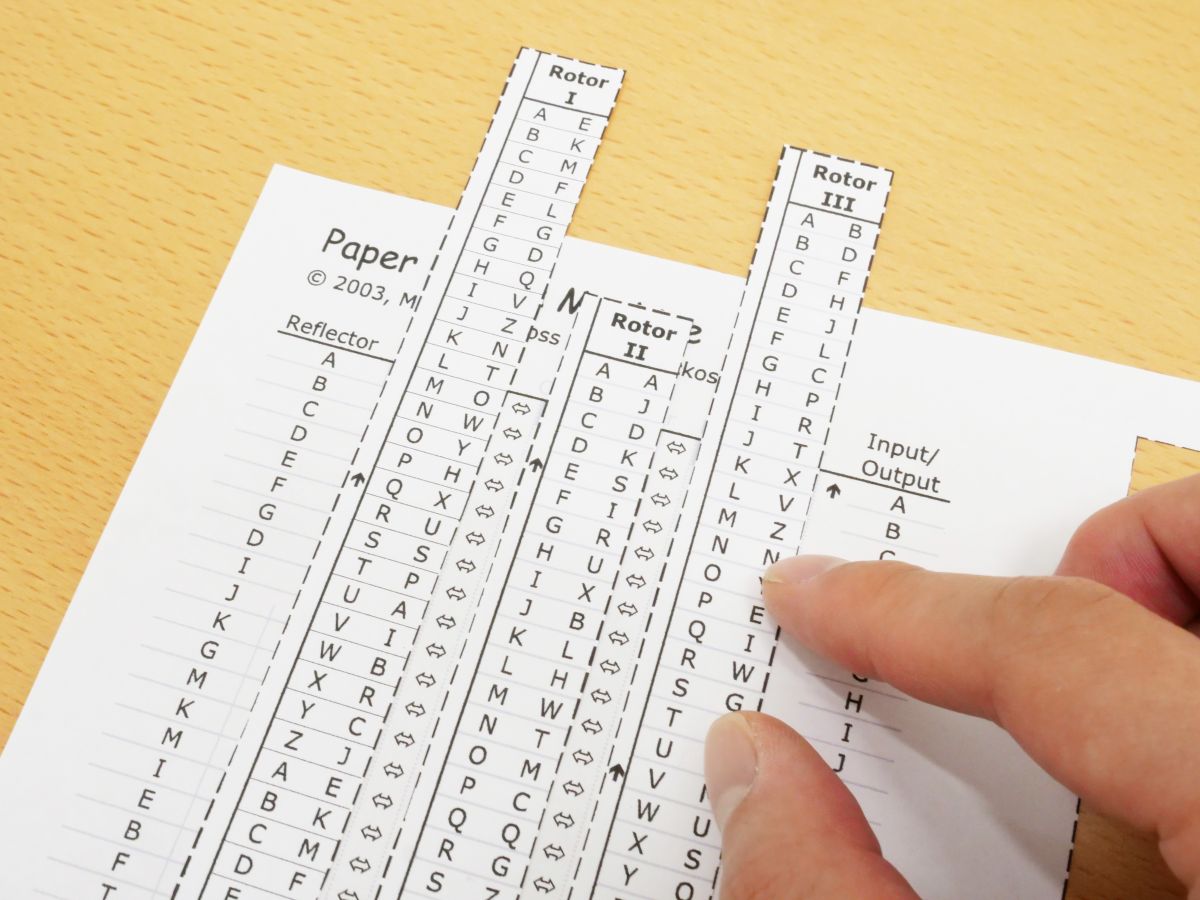



I Tried Using Paper Enigma Machine Which Can Reproduce Nazi Germany S Masterpiece Encryption Machine Enigma With Only One Sheet Of Paper Gigazine



1




Vegetarian Pig Lover A History Of Codes And Ciphers In Code And Cipher



The World According To Benedict Cumberbatch Enigma Chapter 3 The Substitution Cipher
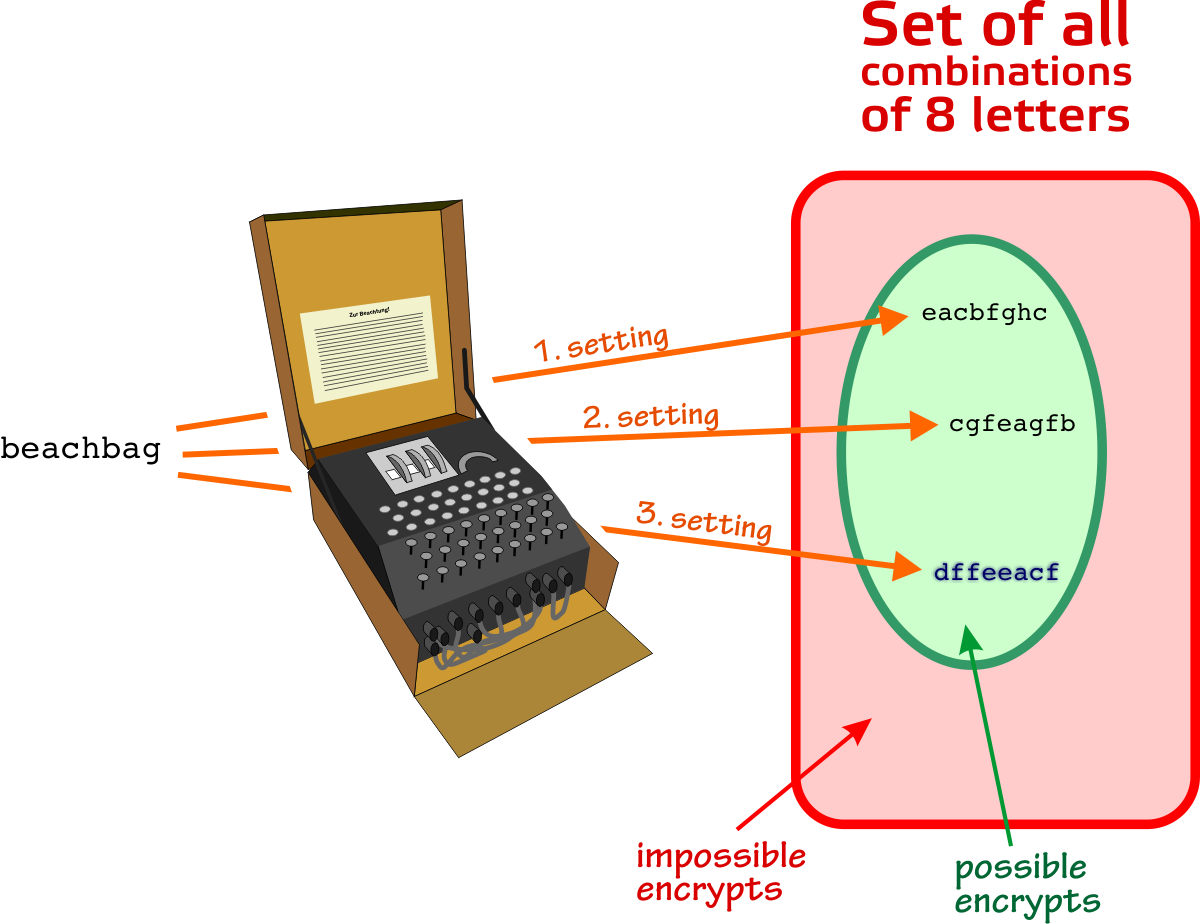



Enigma The German Cipher Machine




A1 Enigma
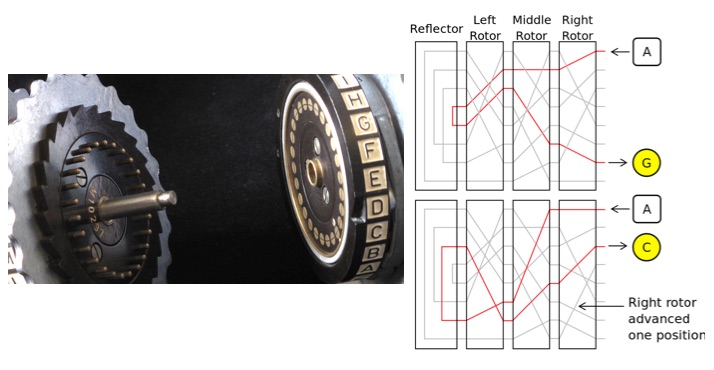



Q How Good Is The Enigma Code System Compared To Today S Publicly Available Cryptography Systems Ask A Mathematician Ask A Physicist
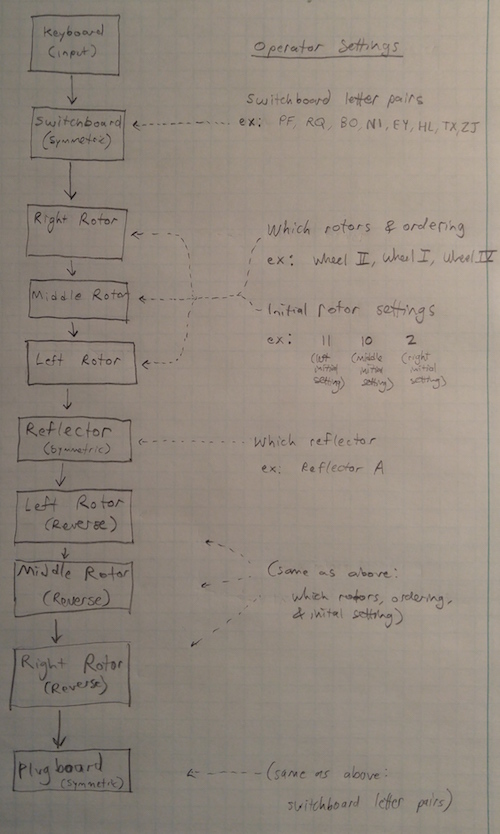



Charlesreid1




Enigma Machine How Does The Famous Encryption Device Work Dev Community



Enigma Procedure



Enigma Cipher



Web Stanford Edu
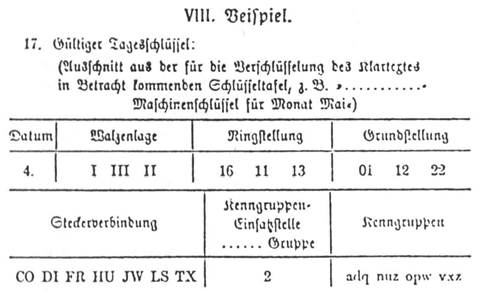



Enigma Codeproject



Web Stanford Edu



1



Why Were There 6 Ways To Arrange The Rotors In The Enigma Machine If All The Rotors Were Similar Contained 26 Letters Quora




The Enigma Cipher Machine And Breaking The Enigma Code
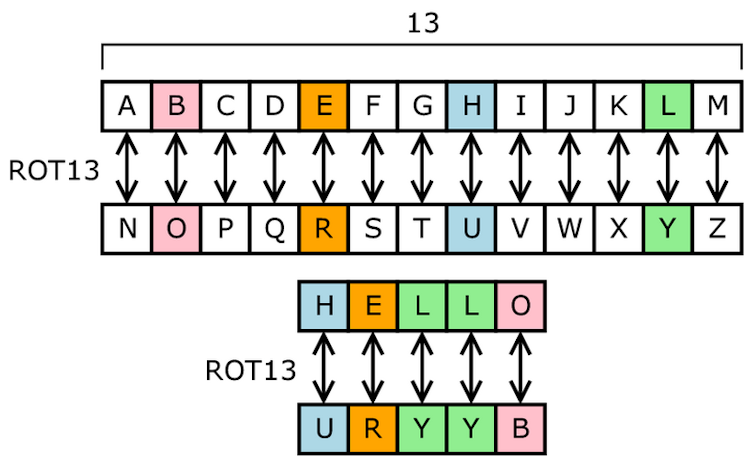



Codebreaking Has Moved On Since Turing S Day With Dangerous Implications




Enigma Codeproject




Pigpen Cipher Wikipedia




Exploring The Enigma Plus Maths Org




Exploring The Enigma Plus Maths Org




Caesar Ciphers




Enigma And A Way To Its Decryption
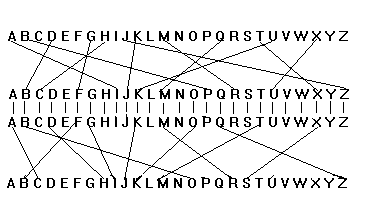



The Enigma 1



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿